Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kojima, Kensuke; Okumura, Keisuke; Okamoto, Tsutomu; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2012/10
A set of the ORIGEN2 library for High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) was newly produced in order to improve prediction accuracy of burn-up characteristics such as spent fuel composition, radioactivity and decay heat. In the library, cross sections and decay data are adopted from JENDL-4.0 and from ENSDF. In the production of effective cross sections and neutron spectrum, MVP-BURN based on the continuous-energy Monte Carlo method and a statistical geometry model is applied to the HTTR fuel with many coated fuel particles. In this way, the double heterogeneous effect of the HTTR fuel can be accurately taken into account. By using the neutron spectrum obtained in the MVP-BURN calculation, infinite dilution cross sections from JENDL-4.0 are condensed to one-group cross sections. The burn-up calculation results of ORIGEN2 with the produced library and those of MVP-BURN with detail modeling and much calculation cost show good agreement for burn-up changes of fuel composition.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Masuro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Design criteria of prismatic High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) in terms of core heat removal capability under depressurized loss-of-forced-circulation accidents without operating active or passive decay heat removal systems are investigated. Lumped element models consist of core, RPV and surroundings and soil are presented in order to evaluate transient response of core and RPV temperatures. The results clarified the design criteria for the Inherently-safe HTGR in terms of core heat removal under DLOFC accidents.
 -H
-H O mixture for IS process
O mixture for IS processTanaka, Nobuyuki; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Asano, Masaharu; Terai, Takayuki*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
Research and development of a water-splitting hydrogen-production method, called iodine-sulfur (IS) process, has been conducting as one of the heat applications of high temperature gas-cooled reactor. Among the unit operations in this IS process, we have investigated electro-electrodialysis (EED) using an ion-exchange membrane to concentrate HI in an HI-I -H
-H O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I
O mixture. Aiming at maximizing EED performance, new membrane materials were prepared by the radiation-induced graft polymerization and were examined in terms of their proton permeability through the membrane, i.e., transport number and conductivity at different iodine (I ) concentrations in the HI-I
) concentrations in the HI-I -H
-H O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I
O mixture. The transport number increased and the conductivity decreased with an increase in the feed I molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I
molality. The EED model derived by the Nernst-Planck theory suggested that this trend could be explained exclusively by the variation of diffusion coefficient of I .
.
 emissions
emissionsKasahara, Seiji; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Nuclear hydrogen steelmaking (NHS) system was evaluated by flow sheet analysis using High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) and thermochemical hydrogen production IS process. Heat input and CO emissions of the system including material production, material transportation, and power generation were evaluation criteria. The result was compared with that of a conventional blast furnace steelmaking (BFS) system. Though total heat input to the NHS system was 141-159% of the BFS system, CO
emissions of the system including material production, material transportation, and power generation were evaluation criteria. The result was compared with that of a conventional blast furnace steelmaking (BFS) system. Though total heat input to the NHS system was 141-159% of the BFS system, CO emissions were 9-17%. Pre-heating of hydrogen by coal combustion before blowing to the shaft furnace was effective to decrease heat input although CO
emissions were 9-17%. Pre-heating of hydrogen by coal combustion before blowing to the shaft furnace was effective to decrease heat input although CO emissions increased a little. Direct nuclear pre-heating was expected to be less heat input without increase of CO
emissions increased a little. Direct nuclear pre-heating was expected to be less heat input without increase of CO emissions if the problems with nearby location of the nuclear reactor to the steelmaking plant would be solved. Influence of hydrogen production thermal efficiency on heat input of the NHS was great. A conceptual design of a plant unit of the NHS system producing steel of 7.43
emissions if the problems with nearby location of the nuclear reactor to the steelmaking plant would be solved. Influence of hydrogen production thermal efficiency on heat input of the NHS was great. A conceptual design of a plant unit of the NHS system producing steel of 7.43 10
10 t/y with a HTGR of 600 MW heat and a shaft furnace and an electric arc furnace was proposed.
t/y with a HTGR of 600 MW heat and a shaft furnace and an electric arc furnace was proposed.
Shimizu, Atsushi; Kawamoto, Taiki; Tochio, Daisuke; Saito, Kenji; Sawahata, Hiroaki; Homma, Fumitaka; Furusawa, Takayuki; Saikusa, Akio; Shinozaki, Masayuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/10
To establish the technical basis of HTGR, the long term high temperature operation using HTTR was carried out during 50-day in 2010. It is necessary to demonstrate the stability of plant during long-term operation and the reliability of components and facilities special to HTGRs, in order to attain the stable supply of the high temperature heat to the planned hydrogen production system of HTTR. Test data obtained in the operation were evaluated for the technical issues which were extracted before the operation. As the results, stability and reliability of the components and facility special to HTGRs was demonstrated by evaluating the heat transfer performance of high temperature components, the helium gas leak tightness, the reliability of the dynamic components such as helium gas circulators, the performance of heat-up protection of radiation shielding. Through the operation, the technical basis for the operation and maintenance technology of HTGRs were established.
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Yan, X.; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Sakaba, Nariaki; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2012/10
All three-gas-circulators are tripped at 9 MW. The primary coolant flow rate is reduced from the rated 45 t/h to 0 t/h. The control rods are not inserted into the core and the reactor power control system does not operated. Analytical results for the reactor transient during the test are presented in this report. It is determined that the reactor power immediately decreases to the decay heat level due to the negative reactivity feedback effect of the core, even though the reactor shutdown system is not operational, and that the temperature distribution in the core changes slowly because of the high heat capacity due to the large amount of core graphite.
Hamamoto, Shimpei; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Furusawa, Takayuki; Nemoto, Takahiro; Inoi, Hiroyuki; Takada, Shoji
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/10
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Yukio; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko; Ogawa, Masuro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2012/10
The concept of the Naturally-safe HTGR is that the release of radioactive materials is kept at very low level and no harmful effect on people and the environment is ensured by only physical phenomena without any engineered safety features. At an air ingress accident, possible physical events to loss of the confinement function of the fuel coating layers are the crack of the coatings caused by the explosion of CO produced by the graphite oxidation and failure of the coatings by melting or sublimation caused by core heat up due to the reaction heat. The CO concentration and the heat generated by graphite oxidation inside the circular tube were numerically evaluated. It was confirmed that the CO concentration at the outlet of coolant channel can be maintained below the explosion limit due to the reaction with oxygen in the air, and the reaction heat can be removed by physical phenomena under certain conditions of the coolant channel geometry without any engineered safety features.
Takada, Shoji; Iigaki, Kazuhiko; Shinohara, Masanori; Tochio, Daisuke; Shimazaki, Yosuke; Ono, Masato; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; et al.
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2012/10
JAEA has carried out research and development to establish the technical basis of HTGRs using HTTR. LOFC test to verify the inherent safety of HTGR under the condition of loss of forced cooling while the reactor shut-down system disabled was initiated. A temperature coefficient of reactivity is one of the important parameters for core dynamics calculations for safety analysis, and changes with burnup because of variance of fuel compositions, which has been measured to confirm the validity of the calculated ones. In order to connect hydrogen production system to HTTR, it is necessary to ensure the reactor safety when thermal-load of the hydrogen production system is lost. Thermal load fluctuation test is planned to demonstrate the reactor safety and gain the test data for validation of the plant dynamics code. It will be confirmed that the reactor become stable state during a part of removed heat at HTTR heat-sink is lost.
Goto, Minoru; Seki, Yasuyoshi; Fukaya, Yuji; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sato, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2012/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has started a conceptual design study of a small-sized High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) with 50 MW thermal power (HTR50S) to be deployed in developing countries in the 2020s. The nuclear design of the HTR50S is performed by upgrading that of a High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR), which is the Japanese HTGR with 30 MW thermal power. In the HTTR design, 12 kinds of fuel enrichment was used to optimize the power distribution. In the previous study of the HTR50S, we succeeded in reducing the number of the fuel enrichment to 3. The present study challenges the nuclear design for effective use of uranium by utilizing high burn-up fuel and axial fuel shuffling, in which a half of the loaded fuel elements is discharged from the core every 2 years and the remains are reloaded. The core burn-up calculations were performed and the nuclear characteristics were confirmed to satisfy the design requirement.
Noguchi, Hiroki; Kubo, Shinji; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Onuki, Kaoru; et al.
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting research and development on a thermochemical iodine-sulfur (IS) process. An examination is planned to verify the integrity of the components in the sulfuric acid decomposition section. A bayonet-type sulfuric acid decomposer made of SiC ceramics, a key component in the section, was test-fabricated. In parallel, a direct-contact heat exchanger (DCHX) is contemplated for use in the sulfuric acid decomposition section to simplify the process. Although the concept is very attractive, little is known about the heat and mass transfer behavior in the DCHX. Therefore, a test apparatus was constructed to measure the gas-phase mass transfer coefficients required for the optimal design of the DCHX. These coefficients of water were acquired and compared with an empirical correlation. The experimental data were in good agreement with those obtained from empirical correlation, and thus, the apparatus was confirmed to be reasonable.
Kamiji, Yu; Terada, Atsuhiko; Takegami, Hiroaki; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2012/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting a conceptual design of electricity and process heat cogeneration system with a small-sized high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR). In this paper, desalination plant was adopted as a heat utilization plant. Heat and mass balance, and thermal efficiency are obtained as a part of conceptual design by Microsoft Excel model for steady state heat and mass balance. Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) process was selected as a desalination method because of its reliability and operational simplicity. In the calculation, the process heat is supplied from third turbine extraction. This paper shows results of sensibility analysis for the small-sized HTGR cogeneration system for desalination. It was found that the impact of the heat distribution rate and extraction condition.
Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Nakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Inaba, Yoshitomo; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 9 Pages, 2012/10
Passive heat removal performance of the reactor vessel cavity cooling system (RCCS) is of primary concern for enhanced inherent safety of HTGR. In a loss of forced cooling accident, decay heat must be removed by radiation and natural convection of RCCS. Thus thermal hydraulic analysis of reactor internals and RCCS is powerful means for evaluation of the heat removal performance of RCCS. The thermal hydraulic analyses using CFD computation tools are conducted for normal operation of the High Temperature Engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) and are compared to the temperature distribution of measured data. The calculated temperatures on outer faces of the permanent side reflector (PSR) blocks are in fair agreement with measured data. The transient analysis for decay heat removal mode in HTTR is also conducted.
 C high temperature gas-cooled reactor
C high temperature gas-cooled reactorNakano, Masaaki*; Takada, Eiji*; Tsuji, Nobumasa*; Tokuhara, Kazumi*; Ohashi, Kazutaka*; Okamoto, Futoshi*; Tazawa, Yujiro; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
The conceptual core design study of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) is performed. The major specifications are 600 MW thermal output, 950 C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release,
C outlet coolant temperature, prismatic core type, enriched uranium fuel. The decay heat in the core can be removed with only passive measures, for example, natural convection reactor cavity cooling system (RCCS), even if any electricity is not supplied (station blackout). The transient thermal analysis of the depressurization accident in the case the primary coolant decreases to the atmosphere pressure shows that the fuels and the reactor pressure vessel temperatures are kept under their safety limit criteria. The fission product release, 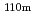 Ag and
Ag and  Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Cs from the fuels under the normal operation is small as to make maintenance of devices in the primary cooling system, such as a gas turbine, without remote maintenance. The HTGRs can achieve the advanced safety features based on their inherent passive safety characteristics.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Kunimoto, Eiji*; Yamaji, Masatoshi*; Eto, Motokuni*; Konishi, Takashi*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
In this study, in order to develop evaluation method for material properties and to evaluate the irradiation-induced property changes under higher neutron doses for IG-430, the oxidation and densification effects on elastic modulus of IG-430 were investigated. Moreover, the correlation of the microstructure based on the X-ray tomography images and the material properties was discussed. It was shown that the elastic modulus of the densified graphite depends on only the closed pores and it is possible to evaluate the material properties of graphite by using X-ray tomography method. However, it is necessary to take into account of the change in the number and shape of closed pores in the grain to simulate the elastic modulus of the highly oxidized and irradiated materials by the homogenization analysis.
Yamada, Teruaki*; Matsushima, Yuki*; Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Fujita, Ichiro*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
In order to investigate the effects of the experimental methodology and the notch angle on the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic nuclear graphites IG-110 and IG-430, the three-point-bending test, which has been recently proposed as the methodology to evaluate the fracture toughness of graphite for high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), was performed using two types of the specimens with different notch angles. The results obtained in this study could be summarized as follows: (1) The values of the fracture toughness of IG-110 and IG-430 measured in this study were 0.890 (MPam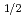 ) and 1.031 (MPam
) and 1.031 (MPam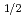 ), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
), respectively. It was also found that the value of the fracture toughness of IG-110 was nearly equal to or smaller than the values obtained by the other method reported previously. (2) The values of the fracture toughness of the fine-grained isotropic graphites were not affected between the notch angles introduced by the incisive razor blade. (3) The ratio of the tensile strengths of IG-110 and IG-430 was estimated from Griffith Theory using the experimental data obtained in this study. The estimated strength ratio was in good agreement with the strength ratio obtained from the supplier's data.
Ueta, Shohei; Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Aihara, Jun; Fujita, Ichiro*; Ohashi, Jun*; Nagaishi, Yoshihide*; Muto, Takenori*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Sakaba, Nariaki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
A new concept of the High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR), so-called the Naturally Safe HTGR, is proposed as a challenge to assure no event sequences to the harmful release of radioactive materials even when the design extension conditions such as the air/water ingress accidents occur by deterministic approach based on the inherent safety features of the HTGR. For the Naturally Safe HTGR it is important to prevent recriticality accidents by keeping the geometry of the fuel rod which consists of the graphite sleeve, fuel compact and SiC-TRISO coated fuel particle, and by improving the oxidation resistance of the graphite when air/water ingress accidents occur. This paper describes the R&D plan for un-irradiation and irradiation test under simulating air/water ingress accident condition to develop oxidation-resistant graphite and to investigate the oxidation behavior of SiC coated fuel particle.
Takegami, Hiroaki; Terada, Atsuhiko; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
Since highly corrosive materials such as sulfuric and hydriodic acids are used in the IS process, JAEA has been developing a sulfuric acid decomposer made of silicon carbide (SiC). One of the key technological challenges for the practical use of a ceramic sulfuric acid decomposer made of SiC is to be licensed in accordance with the High Pressure Gas Safety Act. Since the strength of a ceramic material depends on its geometric form, etc., the strength evaluation method required for a pressure design is not established. In this paper, the minimum strength of SiC components was calculated by Monte Carlo simulation, and the minimum strength evaluation method of SiC components was developed by using the results of simulation. The method was confirmed by fracture test of tube model and reference data. of SiC components was developed by using the results of simulation. The method was confirmed by fracture test of tube model and reference data.
Terada, Atsuhiko; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Kamiji, Yu; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2012/10
We have proposed a hydrogen supply-chain system, which is a supply system of hydrogen produced by HTGR-IS hydrogen production system. The organic chemical hydride method is one of the candidate techniques in the system for hydrogen storage/transportation. In this study, properties of organic hydrides and conventional hydrogen supply system were surveyed to make use of the conceptual design of the hydrogen supply system using an organic hydrides method with VHTR-IS hydrogen production process. It was also clarified the problems of hydrogen supply system, such as energy efficiency and system optimization.
Kubo, Shinji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Noguchi, Hiroki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kasahara, Seiji; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2012/10
Thermochemical iodine-sulfur hydrogen production process is a promising application for the high temperature gas-cooled reactors. To realize this process, one of the key engineering tasks is proof of manufacturability of chemical reactors made of practical structural materials and confirmation of the reactors' sound performance in the harsh working conditions of the process. In order to examine the task, test apparatuses of the process are being constructed by JAEA. The Bunsen section has been built and assembled, the H SO
SO decomposer was recently manufactured, and the HI decomposer will be manufactured in FY2012. Throughput of the test apparatus is equivalent of a hydrogen production rate of 150 NL/h, and the design pressure is 0.95 MPa [abs]. The Bunsen reactor was assembled using corrosion resistant materials such as glass- and fluoroplastic-lined steels. The reactor is required to perform multiple functions of mixing the reactants and recycled substances, producing HI and H
decomposer was recently manufactured, and the HI decomposer will be manufactured in FY2012. Throughput of the test apparatus is equivalent of a hydrogen production rate of 150 NL/h, and the design pressure is 0.95 MPa [abs]. The Bunsen reactor was assembled using corrosion resistant materials such as glass- and fluoroplastic-lined steels. The reactor is required to perform multiple functions of mixing the reactants and recycled substances, producing HI and H SO
SO by chemical reaction, carrying out heat removal, and separating products and gases. The reactor features an outer-circulating, co-current system to perform the said functions via a relatively simple mechanism. At first, performance of chemical reaction will be tested, followed by long-term service test of the reactors to demonstrate the durability of the construction materials. The results are expected to prove the promising engineering advances toward the practical use of Bunsen reactor that is a core device of this process.
by chemical reaction, carrying out heat removal, and separating products and gases. The reactor features an outer-circulating, co-current system to perform the said functions via a relatively simple mechanism. At first, performance of chemical reaction will be tested, followed by long-term service test of the reactors to demonstrate the durability of the construction materials. The results are expected to prove the promising engineering advances toward the practical use of Bunsen reactor that is a core device of this process.
Hania, R.*; M nard, G.*; Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Knol, S.*; De Jong, A.*; Van den Berg, F.*; Van Staveren, T.*; De Groot, S.*
nard, G.*; Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Knol, S.*; De Jong, A.*; Van den Berg, F.*; Van Staveren, T.*; De Groot, S.*
Proceedings of 6th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2012) (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2012/10
The PYCASSO irradiation experiments have been conducted to determine the effect of irradiation at high temperature on the properties of various coating materials of the coated fuel particle. One part of PYCASSO is to evaluate the advanced barrier material ZrC. Pyrocarbon (PyC) / ZrC-coated ZrO and Al
and Al O
O particles fabricated by JAEA were irradiated by HFR at 900
particles fabricated by JAEA were irradiated by HFR at 900  C and 1,100
C and 1,100  C, at the same flux level up to approximately 2 dpa. Samples of irradiated and unirradiated particles are under investigation using an electron microscope, with the aim to identify irradiation effects and the influence of the heat treatment after the fabrication on the ZrC microstructure. Preliminary results of this SEM study indicate that whereas the heat treatment at 1,800
C, at the same flux level up to approximately 2 dpa. Samples of irradiated and unirradiated particles are under investigation using an electron microscope, with the aim to identify irradiation effects and the influence of the heat treatment after the fabrication on the ZrC microstructure. Preliminary results of this SEM study indicate that whereas the heat treatment at 1,800  C prior to irradiation induces significant grain growth near the ZrC edges, embrittling the ZrC layer and weakening the iPyC-ZrC interface, irradiation has no noticeable effect on microstructure and coating strength.
C prior to irradiation induces significant grain growth near the ZrC edges, embrittling the ZrC layer and weakening the iPyC-ZrC interface, irradiation has no noticeable effect on microstructure and coating strength.